Topics related by tag:
- Details
- Computational Cardiology
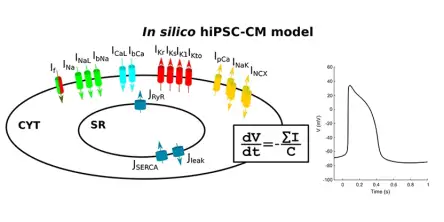
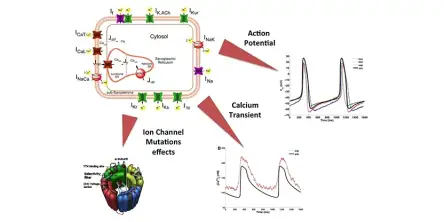
The human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC) technology, discovered in the 2000s, allows us to induce pluripotency and produce stem cells directly from healthy donors and patients. hiPSC-derived cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-CMs) are cardiac cells differentiated from hiPSCs, and they represent a potentially infinite pool of human patient- and disease-specific in vitro models for cardiac studies. Their
- Details
- Molecular Dynamics
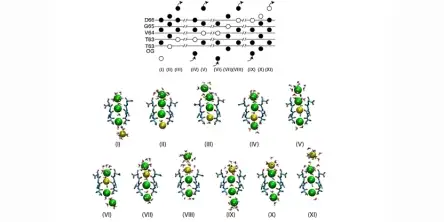
The selectivity of ion channels to different ion species is crucial for important biological processes, as nerve transmission and muscular contraction. Thanks to the availability of experimental atomic structures of several ion channels, including K+-channels, Na+-channels and Ca2+-channels, it is now possible to investigate the microscopic details of conduction and selectivity. As ion conduction
- Details
- Computational Cardiology
The sinoatrial node (SAN) is the normal pacemaker of the mammalian heart. Over several decades, a large amount of data on the ionic mechanisms underlying the spontaneous electrical activity of SAN pacemaker cells has been obtained, mostly in experiments on single cells isolated from rabbit SAN. This allowed the development of comprehensive mathematical models of the electrical activity of rabbit S