All topics
- Details
- Contributed by Chiara Bartolucci
Cardiac mathematical models have gained a relevant role in the investigation of cellular electrophysiology, and several models have been developed to describe the origins of the human cardiac action potential. Variations of electrolyte concentrations in the extracellular fluid, especially for Ca2+ and K+, have a crucial role in the action potential modulation and can ...
- Details
- Published in Computational Cardiology
- Details
- Contributed by Michelangelo Paci
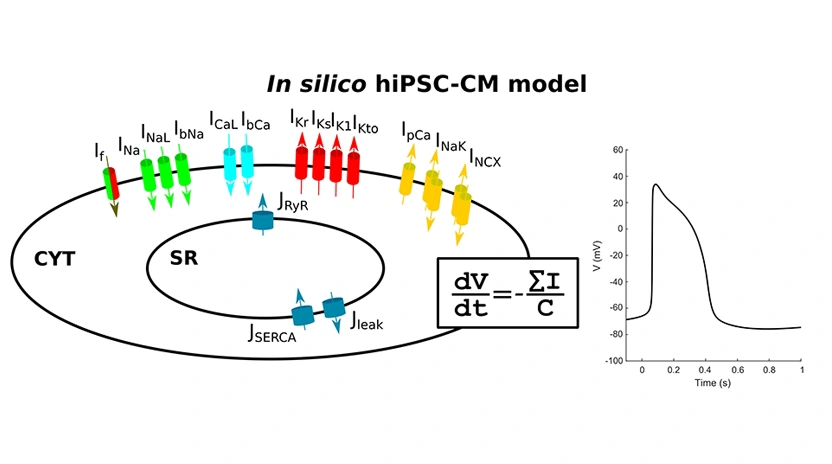
The human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC) technology, discovered in the 2000s, allows us to induce pluripotency and produce stem cells directly from healthy donors and patients. hiPSC-derived cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-CMs) are cardiac cells differentiated from hiPSCs, and they represent a potentially infinite pool of human patient- and disease-specific in vitro models for cardiac studies. ...
- Details
- Published in Computational Cardiology
- Details
- Contributed by Simone Furini
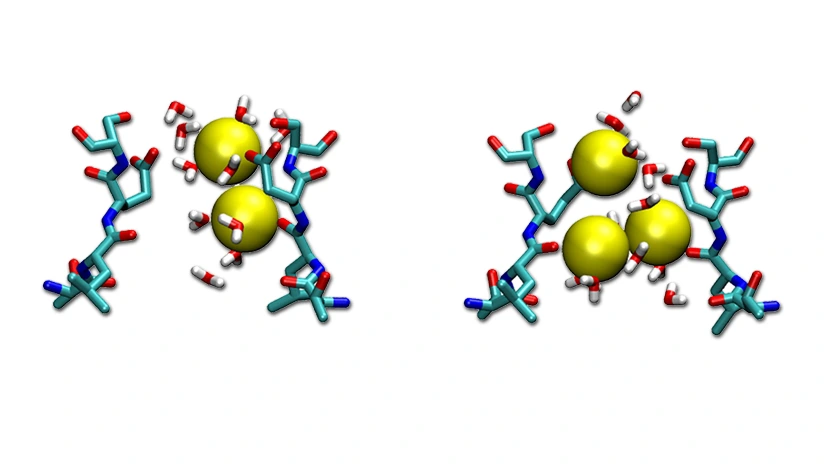
When calculating the free-energy of ions permeating membrane proteins, an initial decision to make is how many ions needs to be included in the calculation. This decision is usually based on previous knowledge (both experiments and simulations), and on the intuition of the researcher. But intuition might be wrong… And taking the number of ions wrong might render free-energy profiles that are ...
- Details
- Published in Molecular Dynamics
- Details
- Contributed by Simone Furini
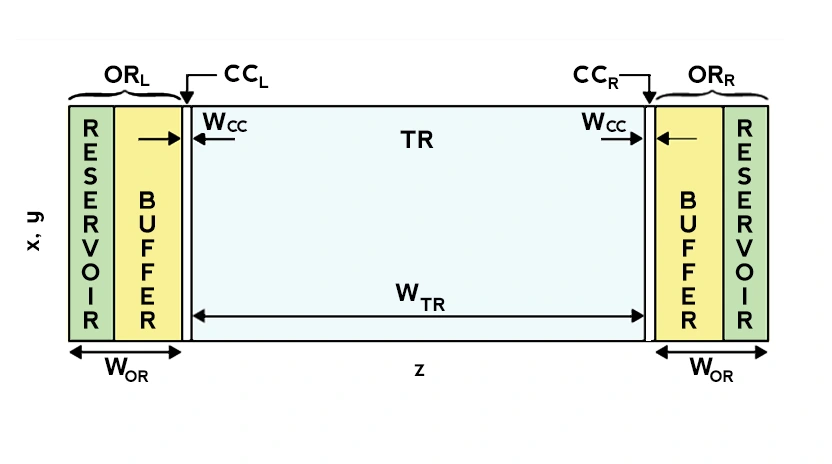
Periodic Boundary Conditions are almost universally adopted in simulations of biological systems at the microscopic scale, in order to replicate as close as possible the experimental environment, while keeping the number of particles to a minimum. While PBC are generally great, they do not allow to simulate gradients in-between the two sides of the simulation box, as these are actually the same ...
- Details
- Published in Molecular Dynamics

- Details
- Contributed by Simone Furini
Na+ channels have high-conductivity to sodium ions, while at the same time being almost completely impermeable to potassium ion. The first characteristic suggests loose atomic interactions between the permeating particles and the channel. On the other hand, it is hard to imagine how selectivity between two similar ion species might be possible under these loose atomic interactions. ...
- Details
- Published in Molecular Dynamics
- Details
- Contributed by Emanuele Giordano
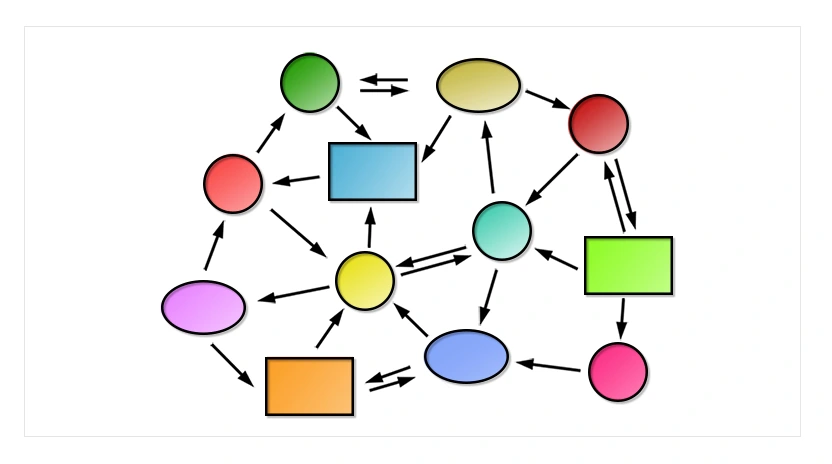
Multidisciplinary approaches prove to be helpful to investigate microenvironmental signals driving cancer cell molecular phenotype. Epithelial to Mesenchymal transition (EMT) has a pivotal role in cancer progression and metastasis formation. Coupling in silico and in vitro analyses, this manuscript gains an insight in the signal transduction cascades driven by a stiff extracellular matrix to ...
- Details
- Published in Systems Biology
- Details
- Contributed by Marilisa Cortese
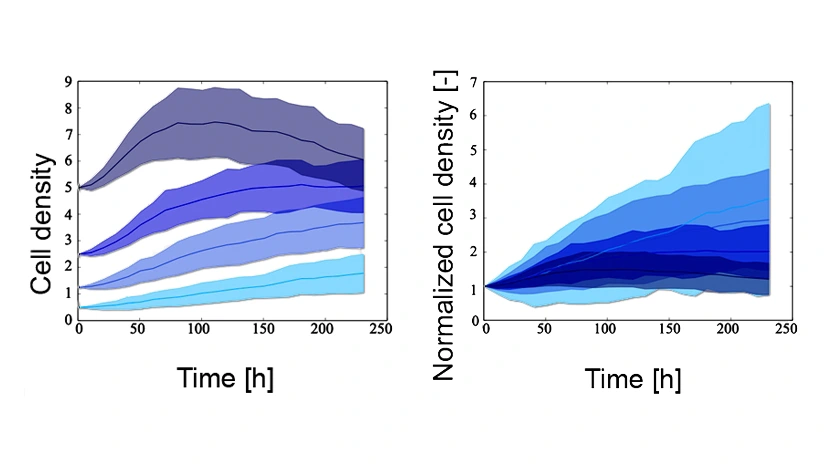
3D cell cultures are becoming increasingly common in-vitro approaches to study cell behaviour in more accurate and realistic settings. The experimental study of these systems, however, is complicated by the lack of non-destructive methods for the quantification of relevant properties like cell density and spatial distribution. Computational simulations can be used to address this limitation and ...
- Details
- Published in Systems Biology
- Details
- Contributed by Marilisa Cortese
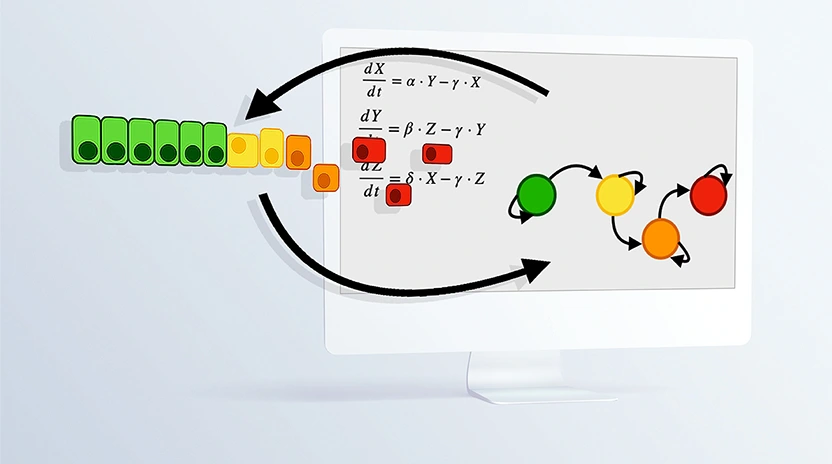
Computational representation of complex biological processes is becoming an increasingly established approach to complement the experimental analysis and study methods to halt/redirect pathological processes. In this review paper we focus on Epithelial to Mesenchymal transition (EMT), a phenotypic transformation with a pivotal role in cancer progression and metastases formation, and present a ...
- Details
- Published in Systems Biology
- Details
- Contributed by Marilisa Cortese
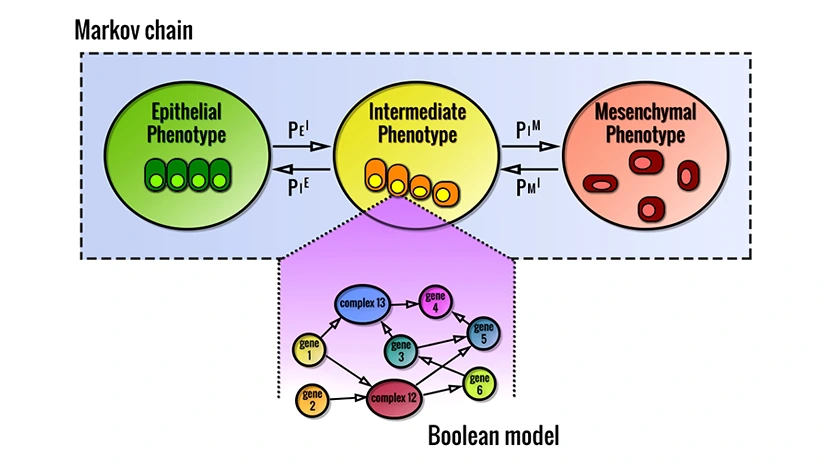
Epithelial to Mesenchymal transition (EMT) is an exceedingly complex biological process that plays a key role in cancer progression and metastases formation. To unravel this complexity and isolate specific genetic markers important for this transition, we have developed a computational model recapitulating both single cell and population behaviours. The former was represented with a boolean ...
- Details
- Published in Systems Biology

- Details
- Contributed by Marilisa Cortese
Transwell assays are another common experimental approach for the quantification of migration and invasion (see also Automatic quantification of (cancer) cell invasiveness). This method relies on a semi-permeable membrane and a layer of Matrigel coating to simulate the extracellular matrix ...
- Details
- Published in Computational Tools
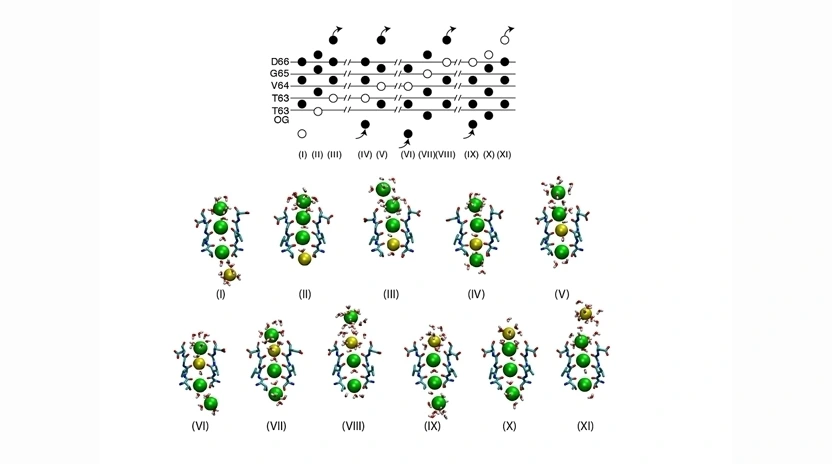
- Details
- Contributed by Simone Furini
The selectivity of ion channels to different ion species is crucial for important biological processes, as nerve transmission and muscular contraction. Thanks to the availability of experimental atomic structures of several ion channels, including K+-channels, Na+-channels and Ca2+-channels, it is now possible to investigate the microscopic details of conduction ...
- Details
- Published in Molecular Dynamics

- Details
- Contributed by Simone Furini
The binding of proteins to DNA controls many cellular events, including gene expression. In order to work properly, DNA binding proteins need to find their target sequences on DNA with high speed and accuracy. The recognition of the specific DNA binding site requires intimate contacts between the protein and the DNA molecule. However, strong atomic interactions between the two molecules are ...
- Details
- Published in Molecular Dynamics