Computational representation of complex biological processes is becoming an increasingly established approach to complement the experimental analysis and study methods to halt/redirect pathological processes. In this review paper we focus on Epithelial to Mesenchymal transition (EMT), a phenotypic transformation with a pivotal role in cancer progression and metastases formation, and present a series of different modeling approaches with alternative objectives (see also Computational model of cell phenotype decision making). In particular, we focus on signal transduction networks, that model how gene expression changes throughout EMT, and on multiscale models, that couple gene expression modelling with frameworks taking into account the cells’ environment and spatial distribution.
Comprehensively this work shows how in recent years the integration of computational and experimental methods has contributed significantly to the study of complex biological phenomena and is expected to become more and more prevalent in the future.
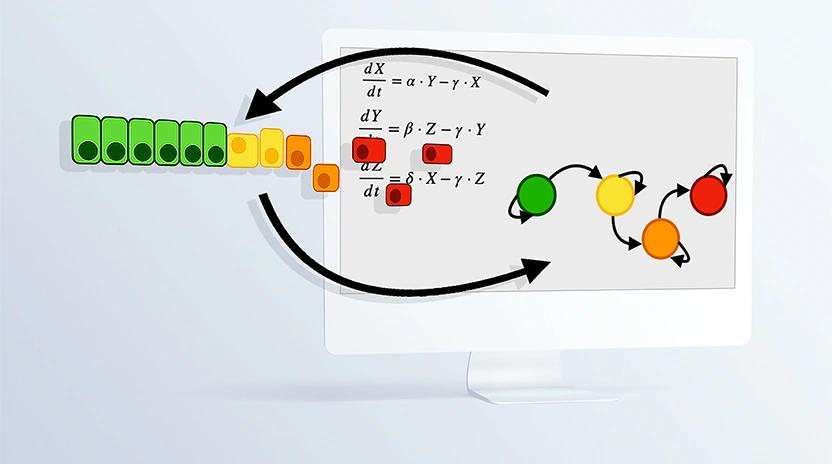
Read the full text at: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/wsbm.1488
This work has also been featured in Advanced Science News: https://www.advancedsciencenews.com/computational-models-a-new-tool-for-cancer-research/
